2023-11-17188

Satellite Internet: Integration of Space and Sky is the Only Way for Future Networks to Achieve Global Seamless Coverage
Source of excerpt: Huaxin Securities
Analyst: Wang Haiming
✓ Introduction to Satellite Internet
Satellite internet is an internet based on satellite communication, which forms a large-scale network by launching a certain number of satellites to radiate the world and build a large satellite system with real-time information processing. It is a new type of network that can provide broadband internet access and other communication services to ground and air terminals, with characteristics such as wide coverage, low latency, broadband, and low cost.
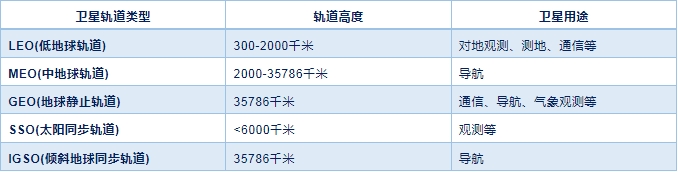
According to orbital altitude, communication satellites mainly include
LEO (Low Earth Orbit), MEO (Medium Earth Orbit), GEO (Geostationary Orbit), SSO (Solar Synchronous Orbit), and IGSO (Inclined Earth Synchronous Orbit).Satellite communication systems built on different orbits have different characteristics in terms of coverage, system capacity, transmission delay, and satellite lifespan. Low orbit satellites are suitable for the development of satellite internet business due to their small transmission delay, low link loss, flexible launch, diverse application scenarios, and low overall manufacturing costs.
Characteristics and Applications of Satellite Orbit Types
✓ Global Satellite Internet Market
From the perspective of market size, according to SIA data, the global satellite internet industry market size increased from 246 billion US dollars to 281 billion US dollars from 2014 to 2022. Although the market growth has fluctuated in the past few years due to the impact of the COVID-19, the market size has increased steadily in 2021 and 2022. In 2022, the global commercial aerospace market reached approximately $384 billion, with the satellite internet industry accounting for 73% of it and still in a dominant position. This indicates that the global satellite internet market is gradually stabilizing and entering a more stable growth stage.
From the perspective of the number of new satellites launched globally,According to UCS data, in 2012, the number of new satellites launched globally was only 132. In 2021, the number of new satellites launched globally reached 1827, with a compound annual growth rate of 33.9% during this period. With the stimulation of demand from the downstream end of the satellite internet, it is expected that the number of satellite launches worldwide will continue to grow in the future.
✓ China's Satellite Internet Market
As of 2022, the number of registered and effectively operating commercial aerospace enterprises in China has reached 433.
According to SIA calculations, the scale of China's satellite internet industry in 2021 is approximately 29.25 billion yuan, and it is expected to rise to 44.692 billion yuan by 2025. The compound growth rate from 2021 to 2025 is 11.2%. Overall, the size of China's satellite internet industry is relatively small and still in the early stage of development. However, it has benefited from multiple policy measures introduced by the government in recent years to encourage the large-scale application of satellite internet in various industries, There are good opportunities for the development of the domestic satellite internet market.
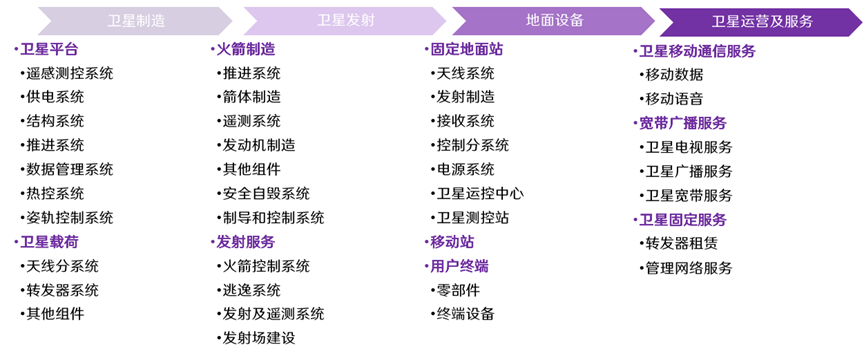
✓ The satellite internet industry chain includes four major links: satellite manufacturing, satellite launch, ground equipment, satellite operation, and services.
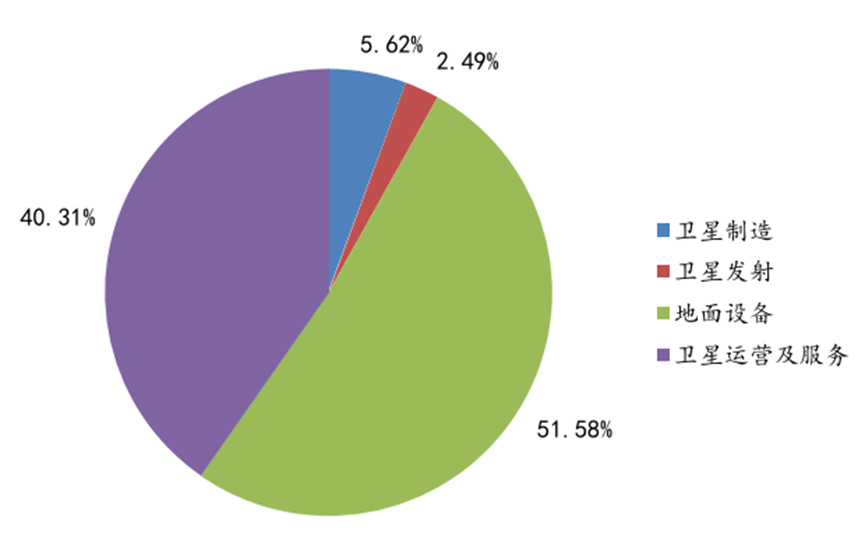
The various links of the industrial chain are constantly exploring and innovating, and are in a period of industrial growth. From the perspective of industry scale in the segmented links of the industrial chain, according to SIA data, satellite manufacturing accounted for about 5.62% of the satellite internet industry chain in 2022, satellite launch accounted for about 2.49%, ground equipment accounted for about 51.59%, and satellite operation and service accounted for about 40.30%. Ground equipment and satellite operation and service in the middle and downstream parts are the two most important parts of the industry chain, accounting for a total market share of about 92.89%. Although satellite manufacturing and satellite launch account for a relatively small proportion of the overall output value, they are still indispensable key links in the entire industrial chain.
卫星互联网产业链
Cost Composition of Satellite Internet Industry Chain
Satellite manufacturing: Payload is the core value
The satellite manufacturing process mainly includes satellite platforms and satellite payloads.
In an ideal state, the cost of satellite platforms ranges from 20% to 30%. Satellite platforms include attitude and orbit control systems, power systems, structural systems, satellite maintenance systems, measurement and control systems, and thermal control systems. Among them, the components and technologies involved in attitude and orbit control systems are the most complex, so their cost proportion is also the highest, accounting for 40% of the total satellite platform.
The attitude and orbit control system can be further divided into:Orbital control system, star sensor, momentum wheel, energy system, solar sensor, control electrical appliances.
The energy system is mainly divided into three types.(1) The traditional satellite energy system is a joint power supply system composed of a solar array and a battery pack. (2) In addition to the traditional solar array battery combined power supply, the power system of manned space vehicles generally also includes a chemical battery power supply and a fuel cell power supply system. (3) Deep space exploration satellites, which have been operating in the dark space for a long time, find it difficult to ensure the lighting conditions of the satellite. Therefore, most of them use nuclear power to power the entire satellite.
The satellite payload is the part of the satellite that performs its core functions after entering orbit, accounting for 70% -80% of the cost. The payload will be adjusted according to the function of the satellite, which is mainly divided into visible light camera payload, phased array radar payload, communication payload, and infrared camera payload according to the various purposes of the satellite.
Satellite launch: rocket hardware costs account for the largest proportion
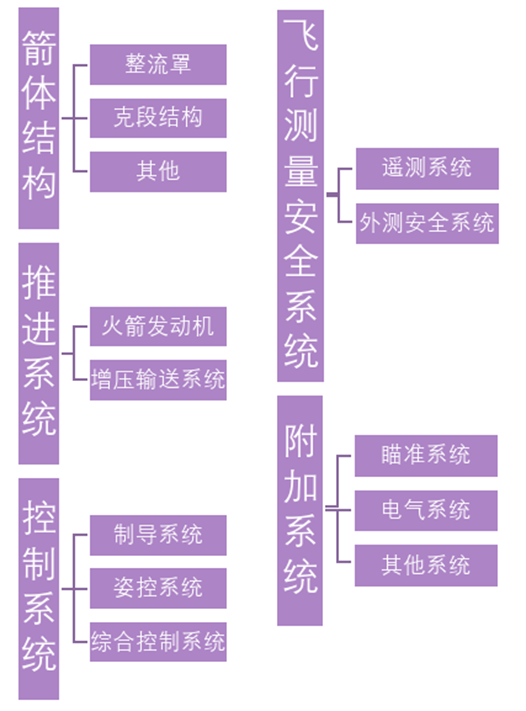
The satellite launch process includes rocket manufacturing and launch services.
The cost of satellite launch mainly consists of rocket hardware cost, direct operating cost, and indirect operating cost.
The hardware cost of rockets accounts for 75% of the launch cost, with direct operating costs such as launch operations and propellants accounting for about 15%, and indirect operating costs such as administrative management and launch site engineering support and maintenance accounting for 10%.
Rocket hardware cost composition
Ground equipment: a wide range of communication products
Ground equipment mainly includes fixed ground stations, mobile stations, and user terminals.
Ground equipment transmits signals to satellites while receiving signals forwarded by satellites, which is a special bridge for communication between the ground and space. Fixed ground station refers to ground equipment fixed on the ground. Mobile stations are carried by ships, planes, and even cars, and are called mobile stations due to the mobility of the vehicle. User terminals refer to satellite television, broadcasting, broadband, and mobile communication equipment.
Fixed ground stationThis includes antenna system, transmission system, reception system, operation and control center, signal terminal, power supply system, measurement and control subsystem, and satellite measurement and control station.
Example diagram of user terminal equipment

Satellite operation and services: 6G integration acceleration, integration of space, space, communication, navigation, and remote control
Satellite operations and services are divided into ground operators and application services.
Satellite communication is an important component of 5G-Advanced and 6G.The large-scale deployment of 5G networks requires high costs, and intensive base station deployment, backhaul network construction, etc. will incur expensive infrastructure costs, as well as installation, leasing, and maintenance costs for optical cables. At the same time, the ground-based network is also difficult to cover geographical areas such as extremely remote areas, oceans, deep ground, sky, and even deep space. Therefore, 5G ground-based network technology is difficult to meet the ubiquitous communication needs of greatly expanding network space. Satellite communication can evolve from 2D population coverage on the surface to 3D global space coverage. The integration of non ground and ground communication systems will directly achieve global 3D coverage, not only providing broadband and wide area Internet of Things services globally, but also supporting new functions such as precise enhanced positioning and navigation, real-time Earth observation, and helping to bridge the "digital divide".
The integration of space and space is the only way for the future network to achieve seamless global coverage.
The demand for multi-dimensional comprehensive information resources in future information services is gradually increasing. The efficient operation of services in areas such as national strategic security, disaster prevention and reduction, aerospace and navigation, education and medical care, environmental monitoring, and traffic management all rely on the comprehensive application of multi-dimensional information such as air, space, and ground. In this context, building an integrated network of space and space, deeply integrating space-based networks, space-based networks, and ground-based networks, fully leveraging the functions of different network dimensions, can break down the barriers to data sharing between independent network systems, achieve wide area full coverage and network interconnection, and meet the future needs of the network for all time, all area, all space communication, and network interconnection. The integrated network structure of space and space is complex and dynamic, and the network construction is complex and costly. It requires a complex network composed of a mixture of multiple heterogeneous networks. The enhancement of satellite communication capabilities is a prerequisite for the evolution of future space space integrated network architecture, and the trend of space space integration is bound to bring incremental satellite communication.
The integration of communication, navigation, and remote sensing refers to the implementation of three functions on a satellite: high-resolution multimode remote sensing, bidirectional IoT communication, and satellite based navigation enhancement.
Satellite communication, satellite positioning and navigation, and satellite remote sensing play a crucial role in various industries. When they form a whole, the efficiency of information acquisition and utilization will be greatly improved. The integration of communication, navigation and remote sensing is an important component and key direction of the current development of communication, navigation and remote sensing systems, and the biggest challenge comes from the addition of satellite remote sensing. Remote sensing satellites will form key nodes in the spatial information network, promoting the interconnection and interoperability of communication, navigation, and remote sensing satellite nodes. By fully leveraging communication transmission, navigation positioning, and remote sensing observation capabilities, the development goal of fast, accurate, and flexible satellite surveying and remote sensing information services will be achieved.
The application prospects of integrated communication, guidance, and remote control are broad. By utilizing the integrated satellite capabilities of "communication, navigation, and remote", natural disaster risk can be transformed from single disaster and single element dispersed monitoring and warning to multi disaster and multi element comprehensive monitoring and warning. Realize intelligent, flat, and integrated emergency rescue command, enhance disaster prevention, reduction, and relief capabilities, handle emergencies throughout the entire process, apply multiple disaster specific topics, and have real-time human influenza awareness and information access capabilities.
--Reprinted to Huaxin Securities